STEM game design is transforming education by offering interactive learning experiences for students. Augmented Reality (AR) is pivotal in this revolution as it bridges the gap between theory and practice. AR-based STEM games are powerful educational tools for improving critical thinking and creativity.
Augmented Reality has the potential to revolutionize STEM education through an effective STEM game design. It allows students to engage with scientific concepts by blending the virtual and physical worlds. According to a report, the AR market is predicted to reach $174.4 billion by 2028.
Projection of AR (Augmented Reality) on STEM game design
Augmented Reality (AR) projection on STEM game design will redefine educational patterns in the coming years. We expect the virtual and physical worlds to become more integrated as technology advances. This integration will lead to smoother and more intuitive learning.

Future AR games will involve complex simulations of real-world scenarios. Learners can manipulate variables and witness the impact in real-time. Engineering students might construct virtual bridges to understand stress and strain principles. Biology students could manipulate DNA strands to observe genetic outcomes.
The Intersection of Augmented Reality and STEM Game Design
Augmented Reality (AR) creates an impressive learning environment by overlaying digital information onto the physical world. AR can bring STEM concepts to life, making them more understandable for students.
AR addresses the resource limitations in traditional classroom environments. With AR, students can virtually dissect a frog, solve a complex mathematical equation, or build a circuit. All within the classrooms or homes need no extra physical resources.
Future Innovations in STEM Game Design Through AR
AR technology can empower learners to interact with and understand complex STEM concepts. AR can give students a more impressive learning experience through game-based learning. It superimposes digital information into the real world.
As technology advances, we expect to see exciting developments to improve learning through STEM Game Design. Some potential future innovations in this field may include:
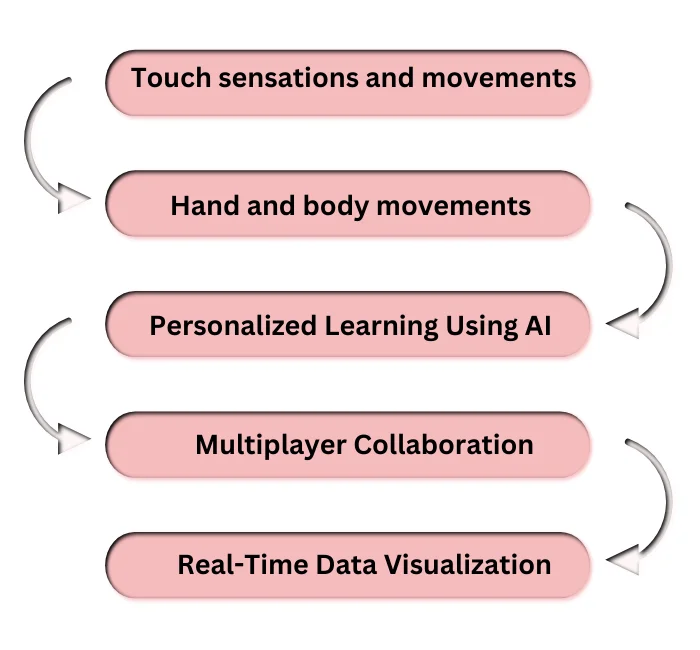
Haptic Feedback
Haptic feedback refers to using touch sensations and movements in virtual environments. Developers can use AR technology to add haptic feedback to STEM games, making the experience more realistic. For example, physics students can feel the impact of forces and interactions when interacting with virtual objects.
Gesture Recognition
Gesture recognition allows people to engage with digital content using hand and body movements. In STEM Game Design, this technology could improve interaction. It enables students to control and manipulate virtual objects with gestures. For example, biology students can dissect virtual organisms or experiment with hand gestures.
Personalized Learning Using AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can enhance personalized learning experiences in AR-based STEM games. AI algorithms can adjust the game to individual needs by analyzing a student’s progress and performance. They provide personalized tasks based on this analysis.
Multiplayer Collaboration
AR technology can create more collaborative and social learning experiences in STEM Game Design. Students can collaborate in a shared virtual environment. They can use their devices to interact and solve complex problems. This will promote teamwork and add fun and competition to the learning process.
Real-Time Data Visualization
AR technology can provide students with real-time visualizations of data. This makes it easier for them to understand complex STEM concepts. For example, chemistry students can visualize molecular structures and reactions in real-time. This enhances their understanding of chemical processes.
Applications of AR in STEM Education
The integration of AR in STEM education is a present reality. Several pioneering applications show the transformative potential of this technology:
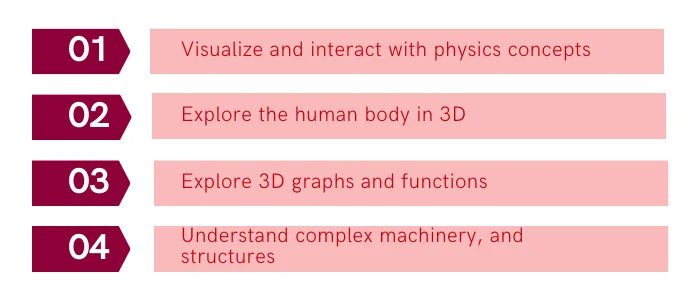
- In physics, AR apps like Physics Studio AR help students visualize and interact with physics concepts. They bring formulae and equations to life.
- AR in biology is revolutionizing the way students study anatomy and physiology. For example, apps like Complete Anatomy allow students to explore the human body in 3D.
- In mathematics, AR offers the unique ability to visualize abstract mathematical concepts. The app GeoGebra AR, for instance, empowers students to explore 3D graphs and functions.
- AR applications such as JigSpace provide interactive 3D models in engineering and technology education. They help students understand complex machinery, circuits, and structures.
Successful Examples of AR in STEM Game Design
Successful examples of the application of AR in STEM game design are:
- Elements 4D: One notable example is “Elements 4D”, an AR mobile game by DAQRI. In this game, players interact with virtual blocks representing different chemical elements. When two blocks are combined, the app shows the chemical reactions, if any, in real-time. This game makes chemistry learning safer and more accessible.
- Zoo-AR: Another example is “Zoo-AR,” a game that allows players to observe virtual animals in their real-world environment. This game can be used to teach students about biology and animal behavior in an immersive and engaging way.
- Minecraft: Education Edition has also introduced AR features. It enables students to place their creations in the real world and examine them from different angles. This feature can be used to teach concepts such as geometry and scale in mathematics and engineering.
Applications of AR Beyond Gaming in the STEM Field
Augmented Reality (AR) is not merely confined to gaming but also significantly impacts other STEM fields. As per a report by PwC, nearly 23 million jobs worldwide will be using AR and VR by 2030 for training, work meetings, or better customer service.
AR is revolutionizing medical education and training in the healthcare sector. It provides medical students with virtual yet realistic scenarios for practicing surgeries. It also helps them understand intricate parts of the human body. This enhances their learning experience and prepares them for real-life medical cases.
In the field of aerospace, organizations like NASA are using AR for equipment repair and maintenance training. It allows trainees to superimpose step-by-step instructions onto the equipment they are working on. In engineering and architecture, AR aids in visualizing architectural designs and blueprints. It accelerates the design process and mitigates errors. It provides a 3D view of the projects, enabling architects to make informed decisions about structural changes.